- What is Trading?
- Trading vs. Investing
- Who Trades and Who Invests?
- Different Types of Trading
- Online Trading vs. Offline Trading
- How Trading Works
- How to Start Trading
- Example of a Trade
- Trading Strategies for Beginners
What is Trading?
Trading is the act of buying and selling financial instruments such as stocks, currencies, and commodities with the goal of making a profit. It plays a key role in the financial markets by providing liquidity and enabling price discovery. Traders speculate on price movements to earn returns, often using platforms like Investopedia or brokerage platforms.
Trading isn’t just about making profits; it’s also about managing risks and making informed decisions based on market conditions. Successful traders know how to strike a balance between opportunity and risk.
Trading vs. Investing
While both trading and investing involve the purchase and sale of financial instruments, they differ in approach and time horizon. Trading typically focuses on short-term gains, while investing is aimed at long-term growth.
| Aspect | Trading | Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Timeframe | Short-term (minutes to months) | Long-term (years to decades) |
| Objective | Profit from price fluctuations | Growth over time, dividends |
| Risk | High due to frequent transactions | Lower, focused on market trends |
To learn more about how trading and investing differ, check out this guide by IG.
Who Trades and Who Invests?
Traders are typically short-term focused, aiming to profit from quick market movements. Investors, on the other hand, buy assets for long-term gains, often holding them for years. Retail traders, institutional traders, and even governments participate in trading markets, while institutional investors like pension funds focus on long-term holdings.
Retail traders accounted for 23% of all US equity trading in 2021, showing the growing impact of individual investors. (Source: StocksToTrade)
Different Types of Trading
- Stock Trading: Buying and selling shares of companies. This is one of the most popular forms of trading.
- Forex Trading: Trading currencies in the foreign exchange market, one of the largest markets globally.
- Commodity Trading: Trading physical assets like gold, oil, and agricultural products.
- Cryptocurrency Trading: Digital asset trading such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Each type of trading has its own characteristics. For instance, forex trading offers high liquidity, while cryptocurrency trading can be highly volatile. Explore the differences in more depth on Forex.com.
Online Trading vs. Offline Trading
Online trading has largely overtaken traditional offline methods. With online trading platforms, you can access global markets instantly, trade from anywhere, and benefit from lower fees. Offline trading, while more personal, involves speaking with a broker directly and can incur higher costs due to commissions.
Online trading platforms such as eToro and Interactive Brokers offer traders access to a wide range of markets, with intuitive interfaces and real-time data, making trading easier and more accessible for beginners.
How Trading Works
The mechanics of trading involve placing orders through a broker, monitoring positions, and closing trades at a profit or loss. Traders use various order types such as market orders, limit orders, and stop-loss orders to manage their positions.
A simple example of a trade would be buying a stock at $100 and selling it when the price reaches $120, pocketing the $20 difference. However, fees, market conditions, and risks can affect the final outcome.
Here’s a simple flow of how a trade is executed:
- Step 1: Place an order through your broker.
- Step 2: Monitor your position using charting tools and market news.
- Step 3: Close the trade when your target price or stop-loss is hit.
To better understand how trading works, visit Investopedia’s trading guide.
How to Start Trading
Getting started with trading can be straightforward if you follow a structured approach. Begin by choosing a market that interests you, such as stocks or forex. Next, select a reliable broker and open a demo account to practice. Lastly, learn technical and fundamental analysis to make informed decisions.
- Pick a market to focus on (stocks, forex, commodities).
- Choose a reliable trading platform, such as Forex.com or eToro.
- Start with a demo account to practice without risking real money.
- Learn technical and fundamental analysis.
For beginners, it’s crucial to start small and gradually increase your capital as you gain experience. Check out this beginner’s guide on BabyPips for more trading tips.
Example of a Trade
Let’s walk through a real-world example. Imagine buying 100 shares of Company X at $50 per share. You believe the stock will rise, so you place a limit order to sell at $55. If the stock hits that price, your trade will close automatically, netting you a $500 profit (excluding fees).
Trading Strategies for Beginners
There are several trading strategies that beginners can explore, each offering a unique approach to the market. Let’s look at three of the most popular strategies:
- Day Trading: This strategy involves buying and selling assets within the same day. Day traders make multiple trades to capitalize on small price movements. It requires constant monitoring of the market and is considered high risk but potentially rewarding. Learn more about day trading on Investopedia.
- Swing Trading: Swing traders hold positions for several days or weeks, attempting to capture short- to medium-term market movements. They use technical analysis to identify trends and entry/exit points. This strategy is less intense than day trading but still demands regular market observation. Check out detailed strategies on StocksToTrade.
- Position Trading: Position traders focus on long-term market trends. They may hold assets for months or even years, making it a lower-risk approach compared to day trading. This strategy is ideal for those who prefer not to monitor the market constantly. More details can be found on Forex.com.
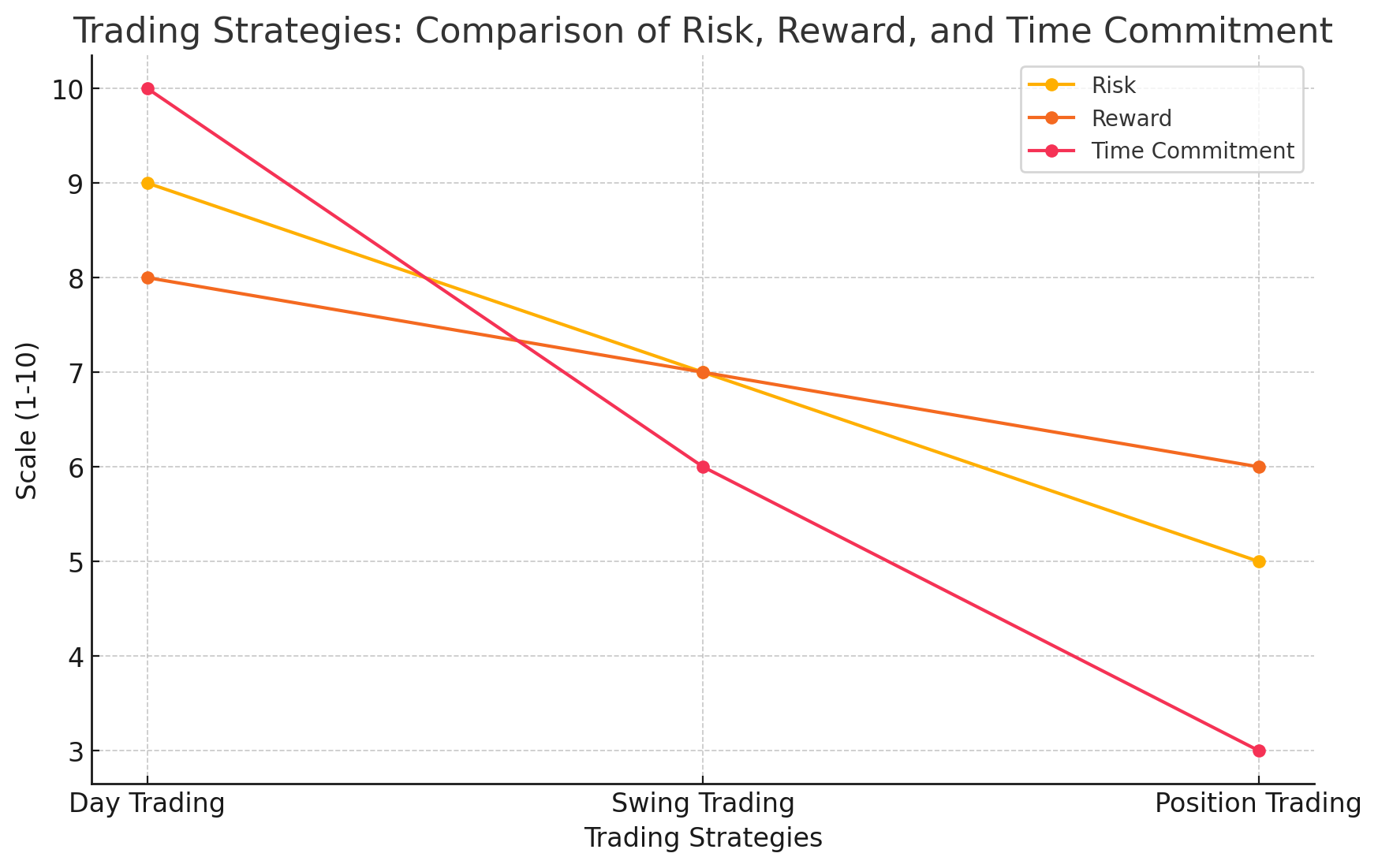
Swing trading offers a balance between short-term volatility and long-term investment. It’s an excellent starting point for those who want to trade actively without the intense time commitment of day trading.
How to Trade for a Living
Trading for a living can be a viable career path, but it requires significant preparation and capital. Here’s how to transition from part-time trading to full-time:
- Build a Safety Net: Have at least six months’ worth of living expenses saved up before you begin trading full-time. This will give you a cushion during periods of market downturns.
- Consistent Strategy: Develop a reliable and tested trading strategy that aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
- Risk Management: Successful full-time traders prioritize risk management, using stop-loss orders and diversifying their portfolio to protect their capital.
Many traders attempt to trade full-time without proper preparation and fail. Make sure you have the financial stability and trading skills needed before taking the plunge. Learn more from The Balance.
Risks Involved in Trading
Trading is inherently risky, and it’s essential to understand the potential pitfalls before diving in. Here are some of the major risks:
- Market Volatility: Prices can fluctuate rapidly, especially in markets like forex or cryptocurrencies, leading to significant losses if trades aren’t managed properly.
- Leverage Risk: Using leverage amplifies both gains and losses. While it allows you to control larger positions with less capital, it can also result in losing more than your initial investment.
- Emotional Trading: Decisions driven by fear, greed, or excitement can lead to poor trading choices. Maintaining a calm and disciplined approach is key to long-term success.
Tools and Resources for Successful Trading
Having the right tools and resources is critical to becoming a successful trader. Here are some of the best tools and platforms to help you along the way:
- Charting Software: Tools like TradingView and MetaTrader 4 offer advanced charting and analysis features to track price movements and identify trends.
- News Feeds: Staying up-to-date with global events is essential for making informed decisions. Use platforms like Bloomberg or Reuters for real-time news updates.
- Economic Calendars: Use an economic calendar like Forex.com to track key financial events and data releases that could impact markets.
Is Trading Right for You?
Trading can be an exciting and potentially profitable venture, but it’s not for everyone. Consider the following to decide if trading suits your personality and financial goals:
- Risk Tolerance: Do you have the emotional resilience to handle market volatility?
- Time Commitment: Do you have the time to monitor trades regularly, or would a more passive investing approach be better?
- Discipline: Are you disciplined enough to stick to a strategy and avoid emotional trading?
If you’re unsure whether trading is right for you, starting with a demo account is a great way to test your skills without risking real money. Platforms like Forex.com and eToro offer demo accounts for beginners.
Conclusion: The Road to Becoming a Successful Trader
Trading offers the potential for significant financial rewards, but it also comes with risks. By starting small, continuously learning, and managing risks wisely, you can navigate the financial markets successfully. Remember, the key to trading success is patience, discipline, and constant education.
Want to learn more? Explore in-depth resources on Investopedia and enhance your trading knowledge before making your first trade.


